Psychological Reasoning

Psychological reasoning is a vital skill for understanding human behavior and improving interpersonal interactions across various fields.
Psychological reasoning refers to the cognitive processes and methods used to understand, analyze, and interpret human thoughts, feelings, and behaviors. It combines principles from psychology to make sense of individual and group dynamics, often applied in various contexts such as therapy, education, and decision-making.
Key Components of Psychological Reasoning
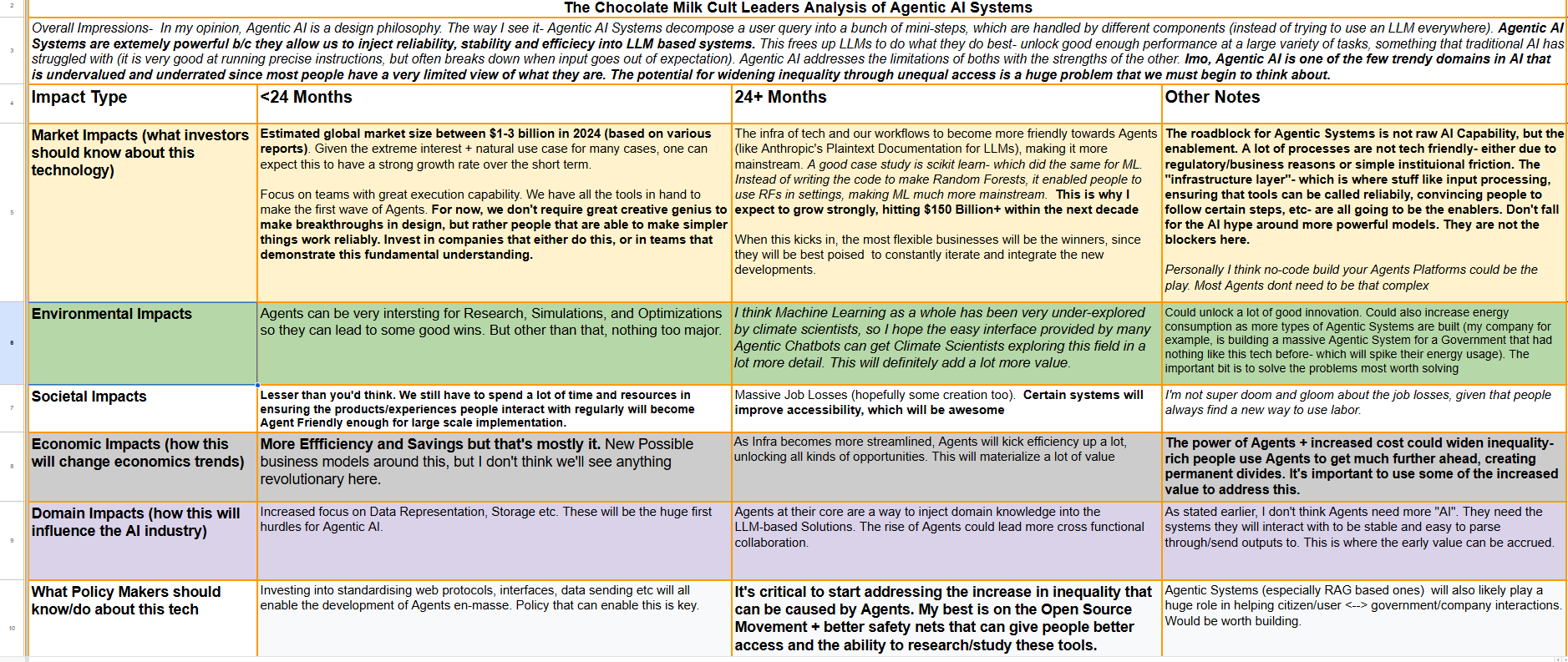
Cognitive Processes: It involves mental activities such as perception, memory, and problem-solving. For example: Analyzing how past experiences influence current behavior.
Emotional Understanding: Recognizing and interpreting emotions in oneself and others. Identifying feelings of anxiety in a client and understanding their impact on behavior.
Behavioral Analysis: Observing and interpreting actions to understand underlying motivations. Noticing avoidance behavior in a student and exploring the reasons behind it.
Social Context: Considering the influence of social interactions and cultural factors on behavior. Evaluating how group dynamics affect individual decision-making. Developmental Perspective -understanding how psychological processes evolve over the lifespan. Assessing how childhood experiences shape adult relationships.
Challenges in Psychological Reasoning
Bias and Subjectivity: Personal biases can distort the interpretation of behaviors or motivations. A therapist's own experiences may influence their understanding of a client's issues.
Complexity of Human Behavior: Human thoughts and actions are often influenced by multiple, interrelated factors. A person’s decision may be impacted by emotional, social, and cognitive factors simultaneously.
Cultural Differences: Cultural contexts shape perceptions and behaviors, complicating interpretations. What is considered assertive behavior in one culture may be viewed as aggressive in another.
Psychological reasoning is a vital skill for understanding human behavior and improving interpersonal interactions across various fields. By integrating cognitive, emotional, and social perspectives, individuals can better analyze situations, facilitate communication, and promote mental well-being. Developing this reasoning enhances empathy and effectiveness in both personal and professional relationships.